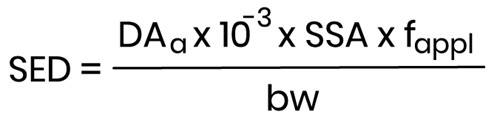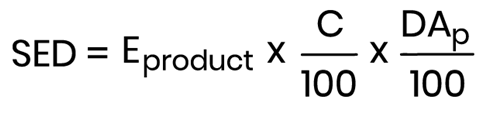Understanding Systemic Exposure Dose (SED) in Cosmetic Ingredient Safety Evaluation
Cosmetic products play a significant role in our daily lives, helping us look and feel our best. Thus, ensuring the safety of these products is of greatest importance and one crucial aspect of the process is the assessment of Systemic Exposure Dose (SED).
What is the Systemic Exposure Dose (SED)?
The Systemic Exposure Dose, abbreviated as SED, is a fundamental concept in toxicology and risk assessment and it refers to the amount of a cosmetic substance expected to enter the bloodstream. It is obtained by combining the external exposure (mg/kg bw/day) with the absorption rate (typically expressed in % or μg/cm2), frequency of application and retention factors and it is expressed in mg/kg body weight/day.
Why does SED matter in cosmetic safety evaluation?
In the context of cosmetics, the SED helps determine the potential health risks associated with the use of certain ingredients. It is essential to assess the SED of cosmetic ingredients to ensure they do not pose any harm when applied to the external parts of the human body (epidermis, hair system, nails, lips and external genital organs) or the teeth and the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
Factors Influencing SED in Cosmetics
Several factors can influence the SED of cosmetic ingredients, including:
- Ingredient physicochemical properties: The chemical composition, size, and solubility of an ingredient can affect its ability to penetrate the skin and enter the bloodstream.
- Frequency and duration of use: The more often a cosmetic product is used and the longer it stays on the skin, the greater the potential for increased SED.
- Ingredient concentration: The concentration of an ingredient in a cosmetic product plays a significant role in SED assessment. Higher concentrations are more likely to result in greater systemic exposure.
How is SED calculated?
Usually, the major route of exposure to cosmetics will be via the skin. There are two ways of calculating the SED, depending on the way the dermal absorption of a substance is reported:
- it is preferably based on the absolute amount bioavailable (µg/cm²) after a certain period, based on the highest anticipated concentration:
Where:
- DAa (μg/cm2) - Dermal Absorption as the amount per surface, resulting from an assay under in-use mimicking conditions;
- SSA (cm2) - Skin Surface Area expected to be treated with the finished cosmetic product;
- fappl (day-1) - Frequency of application of the finished product;
- bw (kg bw) - human body weight
- it may also be based on the percentage dermally absorbed:
Where:
- Eproduct (mg/kg bw/day) - Estimated daily exposure to a cosmetic product per kg (body weight) based on the applied quantity and frequency of application;
- C (%) - Concentration of the substance in the finished cosmetic product;
- DAp (%) - Dermal Absorption as a percentage.
By employing various testing methods and considering factors that influence the SED, regulatory authorities and manufacturers can continue to develop safe and effective cosmetic products for consumers worldwide. Through these rigorous evaluations, we can confidently enjoy the benefits of cosmetic products while minimizing any potential risks to our health.
References:
Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of 30 November 2009 on cosmetic products